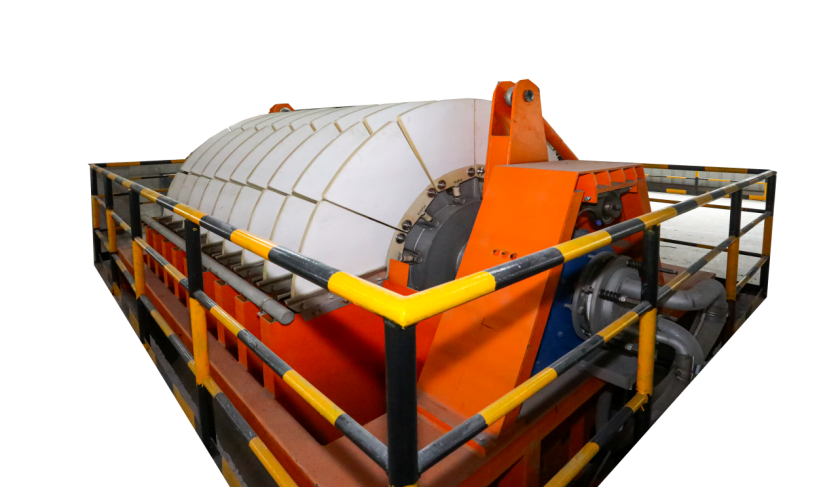
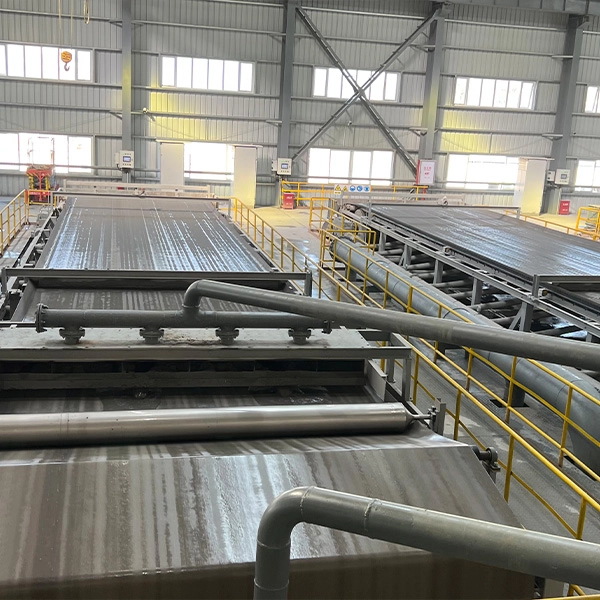
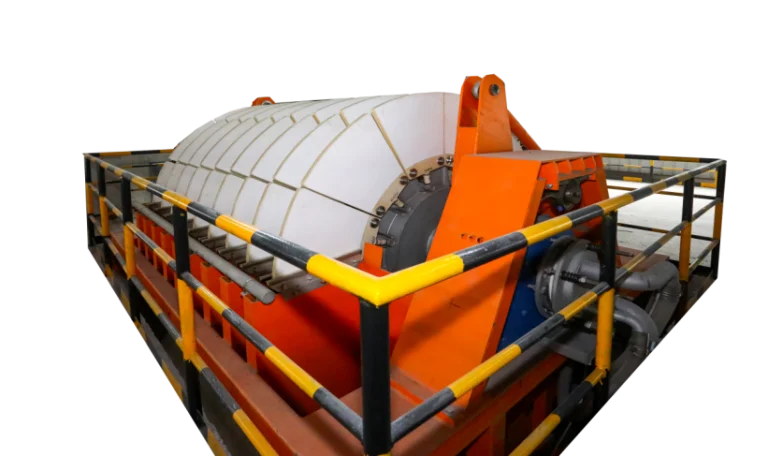
Advancements in Ceramic Filter Materials
Core Properties
Modern ceramic filter materials shine in industry. They have high porosity. This allows fluids to flow through. Impurities get trapped. They resist heat well. They withstand harsh chemicals. Their strength holds up under pressure. They resist wear and abrasion. This ensures a long lifespan. These traits make them vital across sectors.
Material Composition’s Role
The makeup of ceramic filters matters. It drives their performance. Materials like alumina are common. Zirconia and silicon carbide are used too. Each can be adjusted for specific tasks. Silicon carbide handles high heat. It resists thermal shock. Additives enhance performance. Titanium dioxide boosts porosity. Magnesium oxide adds strength. This tailoring optimizes filters for unique needs.
Durability Innovations
New techniques improve filter toughness. Advanced sintering creates dense structures. It reduces cracks. It minimizes flaws. Protective coatings shield surfaces. They block chemical damage. They cut physical wear. Composite materials are emerging. They blend ceramics with other substances. This balances strength and flexibility. These advances extend filter life. They ensure reliability.
Enhancing Filtration Efficiency with Ceramic Filters
Pore Structure’s Impact
Pore design shapes filter success. Uniform pores ensure steady separation. Well-planned pore layouts boost flow. They reduce pressure loss. Microporous ceramics excel at fine filtration. They trap tiny particles. They remove microorganisms. New methods control pore size precisely. This creates specialized filters. They meet specific industry demands.
Surface Treatments’ Effect
Treatments enhance filter performance. They alter how filters interact with substances. Hydrophilic coatings aid water flow. They suit liquid filtration. Hydrophobic treatments work for oil-water splits. Anti-fouling coatings stop buildup. They keep contaminants off surfaces. This cuts maintenance needs. It ensures steady output. Treatments boost efficiency. They add durability.
High-Efficiency Applications
Ceramic filters are key in strict settings. Chemical plants use them. They separate catalysts from mixtures. They purify solvents. Water treatment relies on them. They remove bacteria and heavy metals. They ensure safe drinking water. Pharmaceuticals need them for sterile processes. They maintain product quality. Air purification uses them too. They capture fine dust. They trap harmful gases.
Improving Durability in Ceramic Filter Materials
Corrosion and Wear Resistance
Ceramic filters resist harsh conditions. They don’t react with acids. Alkalines don’t harm them. This suits tough industrial settings. Advanced coatings add protection. They form barriers against corrosion. They shield against wear. Filters stay strong over time. They perform well in aggressive environments.
Thermal Stability’s Value
Ceramic filters handle extreme heat. They keep their shape and function. This suits high-temperature tasks. Flue gas cleaning needs them. Molten metal filtration does too. They endure temperature swings. This prevents breakdowns. It ensures steady operations in critical processes.
Longevity in Tough Settings
Ceramic filters last in harsh conditions. They resist mechanical stress. High pressure doesn’t crack them. They don’t deform easily. Self-healing ceramics are new. They fix small cracks during use. This extends service life. It cuts replacement needs. It improves system reliability. It saves costs.
Applications of Advanced Ceramic Filter Materials
Mining and Metallurgy
Ceramic filters are vital in mining. They separate minerals from slurries. This requires toughness. They resist abrasive wear. They handle harsh chemicals. Acidic solutions are common. Alkaline metals are too. Filters refine molten metals. They remove impurities. This ensures quality products.
Their heat resistance is key. Smelting is intense. Casting involves extreme temperatures. Filters stay reliable. They maintain performance in tough conditions. This makes them essential.
Chemical and Fertilizer Production
Chemical plants rely on precision. Ceramic filters purify solvents. They separate catalysts. Their corrosion resistance is crucial. They handle aggressive chemicals. Custom designs optimize performance. Pore structures fit specific tasks. This boosts efficiency.
Fertilizer production uses them too. They remove impurities from materials. They enhance final products. Abrasive particles don’t harm them. This ensures steady quality. It supports green practices.
Sewage and Tailing Treatment
Sewage plants depend on filters. They remove solids from wastewater. They trap bacteria. They clear contaminants. Microporous designs excel here. They separate fine particles. Effluent meets strict standards. Anti-fouling features cut cleaning needs. Debris doesn’t stick.
In mining, filters treat tailings. They recover water for reuse. They reduce waste volume. This promotes sustainability. Filters handle abrasive slurries. They resist chemical additives. This ensures durability.
Future Trends in Ceramic Filter Material Development
Nanotechnology’s Potential
Nanotechnology transforms filtration. It boosts performance at tiny scales. Nanoparticles enhance filter matrices. Nanoscale coatings improve surfaces. They increase selectivity. They trap ultrafine particles. Heavy metals are removed. Pathogens too. Precise pore control is possible. Filters suit niche tasks. This drives efficiency gains. It sets new benchmarks.
Eco-Friendly Innovations
Sustainability guides filter design. Green production cuts energy use. It reduces waste. Biodegradable components are explored. Recyclable parts are prioritized. Natural raw materials are used. Renewable sources are studied. These align with eco-goals. They make filters greener. Industries value this.
Customization for Industries
Customization is growing. Filters match specific needs. Manufacturers control composition. They adjust pore structures. They tailor surface properties. This suits high-heat tasks in metallurgy. It fits chemical needs in pharmaceuticals. Smart tech is integrated. Sensors track pressure. They monitor temperature. This optimizes performance. It aids maintenance.

Frequently Asked Questions
Which industries use ceramic filters?
Mining, metallurgy, and chemicals benefit. Water treatment and pharmaceuticals too. Fertilizer production relies on them.
How does nanotechnology help?
It controls pore size. It adds selective coatings. It removes tiny contaminants efficiently.
Are eco-friendly filters available?
Yes, green manufacturing is growing. Biodegradable parts are used. Recyclable designs reduce impact.
Can filters be customized?
Yes, manufacturers tailor composition. They adjust pores and surfaces. This meets unique industry needs.
Contact Yantai Hexin Environmental Protection Equipment Co., Ltd. in YEDA, Yantai City. They specialize in belt filters and vertical presses. Their 20 years of expertise deliver innovative solutions!